Novell Cluster Services for Linux and NetWare (Novell Press)
Contents:
From the server adapters a fiber-optic cable runs to a Fibre Channel switch.
You should look into high availability for more than your servers. You'll gain invaluable insight from authors Rob Bastiaansen and Sander van Vugt, two Novell Certified Instructors with day-to-day experience consulting on the topics covered in this book. It provides the fastest data throughput of all technologies discussed here. In a RAID 5 configuration, data is striped across multiple disks and redundancy information is stored on the disks in the array. The switch will still be the single point of failure in this example.
And last but not least, a disk system is attached to the same Fibre Channel switch. Each LUN can be used as if it were one local disk in a server. If you look at Figure 3.
Therefore it is possible to add some redundancy into the SAN. Each server can be equipped with two HBAs, each connected to a separate switch. And the storage can be connected with two cables into these separate switches. When you have such a setup in place, it is important that some sort of management algorithm be included in the SAN to take care of the multiple paths that become available.
This is known as multipath support. Fibre Channel technology can be used to create the largest clusters possible. It provides the fastest data throughput of all technologies discussed here. We are not sure whether we should call it a disadvantage, but for setting up a Fibre Channel SAN special technical skills are needed. Many customers let their hardware resellers set up the SAN for them to the point where LUNs are available to use from the clustering software. After you have set up a physical connection from every server to a storage device, it is important to look at how the disks are being used inside that device.
This can range from a single disk to using hardware RAID redundant array of independent disks or software mirroring configurations. These types of configurations are valid only for really unimportant data that can be missed for a day or two. You could be thinking of an archive that you want to keep online. In the old days there were technologies to keep data available on tape or optical devices with an easy mechanism to collect the data when needed.
Novell Cluster Services for Linux and NetWare
This was called near-line storage. With the availability of inexpensive large IDE disks, it has become possible to store such data online for a fraction of the cost that is required for either a tape library or expensive SCSI disks. In your clustered environment you can use a disk enclosure with MB IDE disks or an iSCSI target server with those disks to store data that is available through the cluster.
But even then we advise you to use one of the technologies described hereafter to create redundancy for your disks. Especially with these not-too-expensive IDE disks, the time to restore data can be brought to zero for only a few hundred dollars. The most widely used technology for disk redundancy and fault tolerance is RAID. We will first explain some terminology here about RAID that we will use in the remainder of this section. An array is a set of combined disks. Two or more disks are grouped together to provide performance improvement or fault tolerance, and such a group is called an array.
As for the operating system that works with that array, we call that a logical disk. First of all, a warning here about RAID 0: With that technology there really is no redundancy. There is performance improvement because the data is striped across multiple disks. But if one disk in a RAID 0 array fails, the entire array becomes unavailable. RAID 1 mirrors disk blocks from one disk to a another disk. This means that every disk block being written to disk is also written to the second disk.
The operating system connecting to the array sees one logical disk. It is the hardware RAID controller that takes care of the mirroring. In this scenario one disk could fail and the logical disk is still available to the operating system.
RAID 1 improves the performance for read operations because data can be read from either disk in the mirror. This type of redundancy is the most expensive in terms of disk usage because it requires a double amount of disk capacity that is effectively needed. It does that for a minimum of two physical disks and also for two other physical disks. It then uses those two virtual logical disks, that are both striped, internally and mirrors them into one logical disk for the operating system. In a RAID 10 configuration it works the other way around: A minimum of two physical disks are first mirrored into a virtual logical disk, and the same happens for two other physical disks, after which the RAID controller stripes data over the virtual disks that are created.
The effect of using these technologies is that they improve performance compared to regular RAID 1 mirroring.
Regular Price: US$ *; Publisher: Novell Press. Description. Need to configure or manage Novell Cluster Services on NetWare, Linux or a mixed. Novell Cluster Services for Linux and NetWare [Rob Bastiaansen, Sander van Vugt] on bahana-line.com *FREE* shipping on qualifying offers. Need to configure or .
In a RAID 5 configuration, data is striped across multiple disks and redundancy information is stored on the disks in the array. The way this works is that when blocks are written to the physical disks, a parity block is calculated for a combination of blocks of physical devices and written to one of the disks in the array. There is no single disk that holds all the parity information; it is striped across the disks in the array. In this configuration one of the disks in the array can fail and still all data is available because it can be reconstructed with the parity information from the remaining disks.
Only when more than one disk fails does the entire array become unavailable. The great advantage of RAID 5 is that the extra disk capacity that is needed is kept to a minimum. For a combination of four disks, only one extra disk is needed. Buying five 72GB disks will provide you with a net GB disk capacity.
The main disadvantage of RAID 5 is that it has a lower performance compared to RAID 1 because of the additional overhead of the striping process, whereas RAID 1 just writes the data to two disks without having to think about that. An important feature of RAID configurations is that they support hot spare disks and sometimes also hot pluggable disks. With the first feature you can have a disk on standby that can be used to replace a disk immediately in case of a failure. If it supports hot-pluggable disks, you can add disks to the server while it is up. Depending on the RAID controller, you can even expand the array online and add the new segments to the operating system online.
These two features are important to look out for when evaluating RAID controllers for your environment. Besides redundancy that comes as hardware in your servers, it is also possible to use the operating system to create redundancy for your disks. The only solution we think could be used in any professional setup is software mirroring. Novell Storage Services supports this at the partition level. It can be used with physical disks but it is also a possible solution to mirror disks that are used with iSCSI.
This is a RAID 1 solution running over the network. In this configuration one node has read-write access to the DRBD device and the other node does not.
You will get better performance because the RAID controller contains its own processor and cache memory to do its job. Also the management and alerting for hardware RAID are better than what you would get in any operating system. With the storage connections in place and the disks configured for high availability, it is time to look at the last part of the storage component of a cluster solution: Not all file systems are cluster aware and thus not all can be used with Novell Cluster Services.
A node that activates a pool on the shared disk writes a flag to that disk to indicate that the pool is in use by that server. Other servers that have access to the shared disk will see that flag set and will not activate the pool. This prevents corruption that could occur when two servers were writing data to the same data area at the same time. Ext3 and ReiserFS are not cluster aware by nature; but they can be mounted on a server and whenever a failure occurs they can be mounted on another node in the cluster.
There are also true Linux cluster-aware file systems available.
What is Kobo Super Points?
In Chapter 8, "Cluster-Enabled Applications," we explain what file systems to use for different types of applications that you can run in your Open Enterprise Server Linux environment. For a cluster with shared storage, a small part of the shared disk, or maybe a special LUN on the SAN that you assign for this purpose, will be used as the Split Brain Detector partition. All cluster nodes write data to this disk to report about their status.
If a cluster node does not respond to network heartbeat packets, it can be given a poison pill by the other nodes in the cluster and remove itself from the cluster. That poison pill is nothing more than a flag that is set on the Split Brain Detector partition. If access to the Split Brain Detector device is interrupted, a node will take itself out of the cluster. The reason for this is that it assumes that this failure has also interrupted access to the other shared data and thus would impact the functionality of the clustered applications.
The other nodes in the cluster will then load the applications. Or that is what should happen. But let us look into what happens if all nodes lose access to the SBD partition. All of them will assume that there is a problem with the shared storage and will take themselves out of the cluster. This situation can occur because of a hardware failure, either because a disk fails or because a Fibre Channel device, such as a switch, fails or an administrator unplugs a SAN cable.
The solution to this problem is to mirror the SBD partition. During installation of Novell Cluster Services, you can select to configure mirroring if a second device that can hold the SBD partition is available. It is also possible to re-create the SBD partition and to select mirroring at that time.
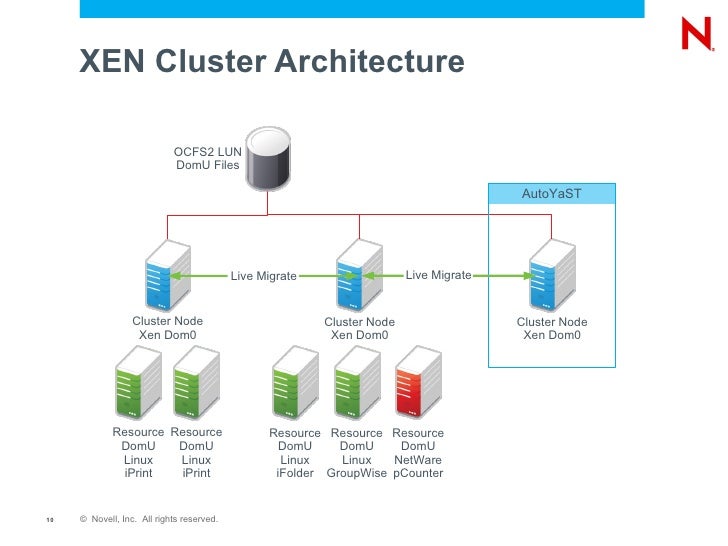
How to do that is discussed in Chapter 9. The way that Novell Cluster Services works is that when a node fails, another node can load the applications that the failed node was running at that time. We call this type of clustering a failover cluster. Other cluster technologies offer a seamless uninterrupted continuation of an application because it is already active on more than one node at a time. So for OES we work with applications that perform a failover. This also has some implications for the type of applications that can be run in a cluster.
Let us first look at a sample application to see how the server and clients behave in a cluster. An Apache web server is running on node 1 and reads its document directory from the shared disk. A user has just loaded a web page from the server and is reading through it. At that time node 1 fails and node 2 activates the shared storage and loads the Apache web server with the exact same configuration and IP address. If the user is finished reading the web page and the server has become online on node 2 in the meantime, the next page the user accesses will be served from node 2 and availability will not be interrupted.
This scheme works for most applications that we can run in the cluster. For example, a user that is accessing GroupWise will not notice if a failover is performed.
- Press Books - Training | Micro Focus!
- Buy Novell Cluster Services for Linux and NetWare - Microsoft Store.
- Join Kobo & start eReading today;
But this will not be true for all types of applications. It depends on the behavior of the application whether the clients will survive a failover. If the web server that we introduced earlier is running a web-based application for a shopping-cart system with server-side session information about shopping baskets and customer information for logged-in customers, all that information, which is very often in memory, will be lost when the node fails, and the customers will have to reestablish their sessions.
Other types of applications that may not survive a failover are databases that run on cluster nodes.
Navigation menu
These will very likely also contain session information about users that are logged in, and the client applications may not support auto-reconnecting to the server. There is no extensive list of applications that can be used as a reference for cluster-enabled applications. But a good starting point is the overview from Novell's documentation website of applications that can be configured for a cluster. The applications known to work well in a Novell cluster are listed here:. For all applications not included in the preceding list, it is up to you as the administrator to test whether they will work in a clustered environment.
You can do that on the test environment that you already are using for your cluster environment. If you do not already have cluster hardware and you want to evaluate whether your applications would work in a cluster, you can also build a cluster in a virtual environment with VMware. Set up My libraries How do I set up "My libraries"?
These 2 locations in All: Federation University Australia - Gippsland campus library. Open to the public. This single location in New South Wales: This single location in Victoria: None of your libraries hold this item. Found at these bookshops Searching - please wait We were unable to find this edition in any bookshop we are able to search. These online bookshops told us they have this item: Tags What are tags? Public Private login e. Lists What are lists? Login to add to list.
- Youre Addicted to You: Why Its So Hard to Change - And What You Can Do about It
- Bad Girls of the Bible: And What We Can Learn From Them
- The Complete Civil War Road Trip Guide: 10 Weekend Tours and More than 400 Sites, from Antietam to Z
- Perspectives on Investment Management of Public Pension Funds (Frank J. Fabozzi Series)
- Bardenklänge Vol.11 - Guitar
- Blue Iris: Poems and Essays
- A Companion to Wolves (Iskryne)