Exercise Physiology
Contents:
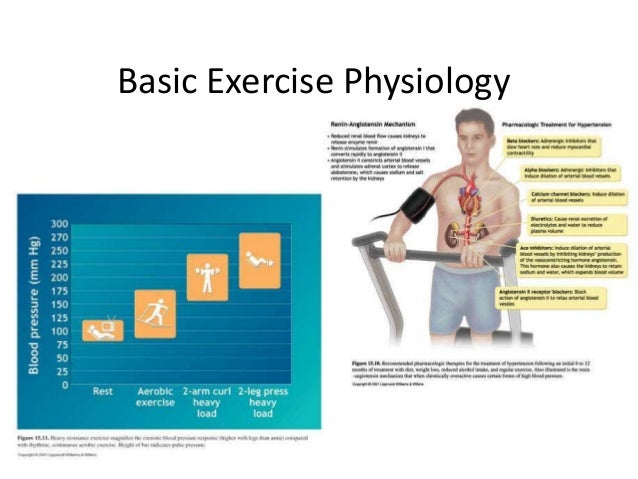
The first-line physiologic response to this demand is an increase in heart rate , breathing rate , and depth of breathing. Oxygen consumption VO 2 during exercise is best described by the Fick Equation: More simply put, oxygen consumption is dictated by the quantity of blood distributed by the heart as well as the working muscle's ability to take up the oxygen within that blood; however, this is a bit of an oversimplification. Although cardiac output is thought to be the limiting factor of this relationship in healthy individuals, it is not the only determinant of VO2 max.
That is, factors such as the ability of the lung to oxygenate the blood must also be considered. In addition, the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood is also an important determinant of the equation. Oxygen carrying capacity is often the target of exercise ergogenic aids aids used in endurance sports to increase the volume percentage of red blood cells hematocrit , such as through blood doping or the use of erythropoietin EPO.
Furthermore, peripheral oxygen uptake is reliant on a rerouting of blood flow from relatively inactive viscera to the working skeletal muscles, and within the skeletal muscle, capillary to muscle fiber ratio influences oxygen extraction. Dehydration refers both to hypohydration dehydration induced prior to exercise and to exercise-induced dehydration dehydration that develops during exercise.
The latter reduces aerobic endurance performance and results in increased body temperature, heart rate, perceived exertion, and possibly increased reliance on carbohydrate as a fuel source. Although the negative effects of exercise-induced dehydration on exercise performance were clearly demonstrated in the s, athletes continued to believe for years thereafter that fluid intake was not beneficial.
The effects of hypohydration may vary, depending on whether it is induced through diuretics or sauna exposure, which substantially reduce plasma volume, or prior exercise, which has much less impact on plasma volume. Hypohydration reduces aerobic endurance, but its effects on muscle strength and endurance are not consistent and require further study.
A male marathon runner loses each hour around 0.
What is exercise physiology? Clearing up the confusion about this multifaceted career
The brain as a result is highly sensitive to failure of its oxygen supply with loss of consciousness occurring within six to seven seconds, [23] with its EEG going flat in 23 seconds. Protecting the brain from even minor disruption is important since exercise depends upon motor control , and particularly, because humans are bipeds, the motor control needed for keeping balance. Indeed, for this reason, brain energy consumption is increased during intense physical exercise due to the demands in the motor cognition needed to control the body.
Cerebral autoregulation usually ensures the brain has priority to cardiac output, though this is impaired slightly by exhaustive exercise. In adults, exercise depletes the plasma glucose available to the brain: At rest, energy for the adult brain is normally provided by glucose but the brain has a compensatory capacity to replace some of this with lactate.
Humans use sweat thermoregulation for body heat removal, particularly to remove the heat produced during exercise. Moderate dehydration as a consequence of exercise and heat is reported to impair cognition. Researchers once attributed fatigue to a build-up of lactic acid in muscles. The action potentials that cause this require also ion changes: Na influxes during the depolarization phase and K effluxes for the repolarization phase. During intense muscle contraction, the ion pumps that maintain homeostasis of these ions are inactivated and this with other ion related disruption causes ionic disturbances.
This causes cellular membrane depolarization, inexcitability, and so muscle weakness. After intense prolonged exercise, there can be a collapse in body homeostasis. Some famous examples include:. Tim Noakes , based on an earlier idea by the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine winner Archibald Hill [47] has proposed the existence of a central governor. In this, the brain continuously adjusts the power output by muscles during exercise in regard to a safe level of exertion.
These neural calculations factor in prior length of strenuous exercise, the planned duration of further exertion, and the present metabolic state of the body. This adjusts the number of activated skeletal muscle motor units, and is subjectively experienced as fatigue and exhaustion. The idea of a central governor rejects the earlier idea that fatigue is only caused by mechanical failure of the exercising muscles " peripheral fatigue ".
Instead, the brain models [48] the metabolic limits of the body to ensure that whole body homeostasis is protected, in particular that the heart is guarded from hypoxia, and an emergency reserve is always maintained. Prolonged exercise such as marathons can increase cardiac biomarkers such as troponin , B-type natriuretic peptide BNP , and ischemia-modified aka MI albumin. This can be misinterpreted by medical personnel as signs of myocardial infarction , or cardiac dysfunction. In these clinical conditions, such cardiac biomarkers are produced by irreversible injury of muscles.
What is exercise physiology? Clearing up the confusion about this multifaceted career
In contrast, the processes that create them after strenuous exertion in endurance sports are reversible, with their levels returning to normal within hours further research, however, is still needed. Humans are specifically adapted to engage in prolonged strenuous muscular activity such as efficient long distance bipedal running. Central to the success of this is the ability of the human body, unlike that of the animals they hunt, to effectively remove muscle heat waste.
In most animals, this is stored by allowing a temporary increase in body temperature. This allows them to escape from animals that quickly speed after them for a short duration the way nearly all predators catch their prey. Humans, unlike other animals that catch prey, remove heat with a specialized thermoregulation based on sweat evaporation. One gram of sweat can remove 2, J of heat energy. This skin based cooling has resulted in humans acquiring an increased number of sweat glands , combined with a lack of body fur that would otherwise stop air circulation and efficient evaporation.
Rodents have been specifically bred for exercise behavior or performance in several different studies. Physical exercise may cause pain both as an immediate effect that may result from stimulation of free nerve endings by low pH, as well as a delayed onset muscle soreness.
- Beautiful Security: Leading Security Experts Explain How They Think?
- Category:Exercise physiology - Wikipedia.
- Exercise physiology!
- What is exercise physiology?.
- Planning Your Marriage: A Workbook Guide for Engaged and Married Couples?
- Exercise physiology - Wikipedia;
The delayed soreness is fundamentally the result of ruptures within the muscle, although apparently not involving the rupture of whole muscle fibers. Muscle pain can range from a mild soreness to a debilitating injury depending on intensity of exercise, level of training, and other factors. Accreditation programs exist with professional bodies in most developed countries, ensuring the quality and consistency of education. In Canada, one may obtain the professional certification title — Certified Exercise Physiologist for those working with clients both clinical and non clinical in the health and fitness industry.
An exercise physiologist's area of study may include but is not limited to biochemistry , bioenergetics , cardiopulmonary function, hematology , biomechanics , skeletal muscle physiology, neuroendocrine function, and central and peripheral nervous system function. Furthermore, exercise physiologists range from basic scientists, to clinical researchers, to clinicians, to sports trainers.
Colleges and universities offer exercise physiology as a program of study on various different levels, including undergraduate, graduate, and doctoral programs. The basis of Exercise Physiology as a major is to prepare students for a career in field of health sciences. A program that focuses on the scientific study of the physiological processes involved in physical or motor activity, including sensorimotor interactions, response mechanisms, and the effects of injury, disease, and disability.
Clinical benefits
Includes instruction in muscular and skeletal anatomy; molecular and cellular basis of muscle contraction; fuel utilization; neurophysiology of motor mechanics; systemic physiological responses respiration, blood flow, endocrine secretions, and others ; fatigue and exhaustion; muscle and body training; physiology of specific exercises and activities; physiology of injury; and the effects of disabilities and disease. Anyone with chronic pain or other health conditions, or anyone at risk of a health condition such as someone with pre-diabetes or with a family history of cardiovascular disease might like to see an EP about how an exercise routine can help prevent, manage or treat their symptoms.
Natalie Delana also says that exercise physiology can be of particular help for people with mental illnesses and conditions such as depression. Because EPs receive a broad medical training, they are skilled in understanding how physical exercise interacts with physiological and psychological conditions. Your EP will tailor your program to your individual needs, tastes and preferences, they will take your exercise history into account and ensure your program is at an appropriate starting level. EPs will also work with you to integrate exercise programs into your everyday activities and lifestyle.
While your exercise physiologist can give you your program and work with you on a regular basis, it is likely they will expect you to do some work on your own or at home. They will help you find the easiest, most enjoyable ways to do this. EPs are recognised professionals in the allied health sector, and trained to prescribe exercise for specific clinical conditions. Personal trainers generally work with people who are already healthy, and do not prescribe exercise for the relief or management of medical symptoms.
HammondCare offers exercise physiology services at our hospitals and in our Hammondville residential aged care homes. Prior to this David had been very active, especially for an year old — he cares for his wife full-time, and played golf at a competitive level. Understandably, he hoped to return to this lifestyle after the hip replacement surgery.
Exercise physiologists play a crucial role in the health and wellness of individuals of all ages and physical capacities. To that end, exercise physiology programs across the country require rigorous academic preparation. The program at The College of St. Scholastica CSS is built upon a foundation of ethical principles and professionalism.

If you're looking for a way to use your knowledge, skills and interests to improve the physical lives of others with a fulfilling career, check out CSS' exercise physiology program page to learn more about degree outcomes, state-of-the-art labs and personalized student exercise programs. The College of St. Scholastica The College of St. Scholastica is an independent private Catholic Benedictine college with locations across Minnesota, in addition to many high-quality programs available online and through convenient evening and weekend formats.
- Afterlife.
- Flora Domestica or The Portable Flower Garden.
- Promise, Trust and Evolution: Managing the Commons of South Asia.
- Exercise physiology.
- Lost in a Good Book: Thursday Next Book 2.
- Exercise Physiology - Definition, History and Career | Biology Dictionary?
Scholastica has been preparing students for a life of purpose and economic gain by engaging students in the love of learning and active citizenship in the world. Our mission is to provide intellectual and moral preparation for responsible living and meaningful work. Diagnosing the differences Many consider physical therapy and occupational therapy to be interchangeable.
Medical professionals would disagree.
Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise. It is the study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to a wide range of exercise conditions. Exercise physiology is "the identification of physiological mechanisms underlying physical activity, the comprehensive delivery of treatment services concerned.
So what's the difference? Check out six of your options!
The future looks bright for physical therapy majors The U. Department of Labor recently released a report on the 20 fastest growing occupations projected through What is exercise physiology?